Wet lung was not known in the medical world, the term is only familiar to the general public. The
term wet lungs is called pneumonia in medical language, which is an
infection of one or both lungs which is usually caused by bacteria,
viruses, or fungi. Before the discovery of antibiotics, a third of all the people who developed pneumonia subsequently died from infection. Currently,
Although most infected people recover wet lung disease, approximately
5% of them had a poor prognosis that can lead to death. In the United States of Lung wet death rate ranks sixth.
Some cases of wet lung occurs by inhaling tiny droplets containing the organism that can cause pneumonia. These droplets get into the air when someone infected with the bacteria through coughing or sneezing. In other cases, is caused when bacteria or viruses that are normally present in the mouth, throat, or nose inadvertently enter the lung. Typically, the reflex response of the body and their immune system will prevent the aspirated organisms from causing organisms pneumonia
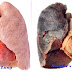
Once the organism enters the lungs, they usually stay in the air sacs and passages of the lungs where they are growing rapidly in number. In the area of lung then becomes filled with fluid and pus (inflammatory cells of the body) as the body attempts to fight the infection.
What Symptoms and Signs of Lung Wet?
Most people who develop symptoms of lung wet to make them cold, followed by high fever, chills, and cough with sputum production. Sputum is usually discolored and sometimes bloody. When the infection settles in the airways, coughing and phlegm symptoms tend to dominate. In some cases of lung wet, spongy tissue of the lungs that contain air bags become more involved. In this case, the oxygenation of the blood can be disrupted, leading to the lungs become stiff, causing shortness of breath. This can cause the sufferer to change the color of his skin became dusky or purplish (a condition known as "cyanosis") due to a lack of oxygen their blood.
Chest pain in wet lung disease may develop if the outer aspects of the lungs near the pleura (lung cavity). This pain is usually sharp and worsens when taking a deep breath and is known as pleuritic pain or pleurisy. In other cases, symptoms of pneumonia depends on the causative organism, and so forth.
Some cases of wet lung occurs by inhaling tiny droplets containing the organism that can cause pneumonia. These droplets get into the air when someone infected with the bacteria through coughing or sneezing. In other cases, is caused when bacteria or viruses that are normally present in the mouth, throat, or nose inadvertently enter the lung. Typically, the reflex response of the body and their immune system will prevent the aspirated organisms from causing organisms pneumonia
Once the organism enters the lungs, they usually stay in the air sacs and passages of the lungs where they are growing rapidly in number. In the area of lung then becomes filled with fluid and pus (inflammatory cells of the body) as the body attempts to fight the infection.
What Symptoms and Signs of Lung Wet?
Most people who develop symptoms of lung wet to make them cold, followed by high fever, chills, and cough with sputum production. Sputum is usually discolored and sometimes bloody. When the infection settles in the airways, coughing and phlegm symptoms tend to dominate. In some cases of lung wet, spongy tissue of the lungs that contain air bags become more involved. In this case, the oxygenation of the blood can be disrupted, leading to the lungs become stiff, causing shortness of breath. This can cause the sufferer to change the color of his skin became dusky or purplish (a condition known as "cyanosis") due to a lack of oxygen their blood.
Chest pain in wet lung disease may develop if the outer aspects of the lungs near the pleura (lung cavity). This pain is usually sharp and worsens when taking a deep breath and is known as pleuritic pain or pleurisy. In other cases, symptoms of pneumonia depends on the causative organism, and so forth.








0 comments: