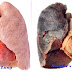
The heart is one of the vital organs of the body whose function is to pump blood throughout the body clean and dirty blood to the lungs. If an interruption in the heart of the blood pumping function can be disrupted even result in death.
A. Arrhythmias
Arrhythmia was defined as abnormal cardiac electrophysiology and cardiac conduction system abnormalities, especially. Arrhythmia is a disorder of the formation and / or drop-off impulse.
Symptoms - symptoms of arrhythmias are:
- Dizziness
- Shortness of breath or chest pain
- Fatigue
- Patients are confused
What causes an arrhythmia?
· Inflammation of the heart, such as rheumatic fever, myocardial inflammation (myocarditis due to infection).
· Impaired coronary circulation (coronary atherosclerosis or coronary artery spasm), such as myocardial ischemia, myocardial infarction.
· Because of the drug (intoxication), among others, by digitalis, quinidin, and anti-arrhythmia drugs other.
· Impaired balance of electrolytes (hyperkalemia, hypokalemia).
· Disorders of the autonomic nervous system settings that affect the work and the rhythm of the heart.
· Disturbance psikoneurotik and central nervous system.
· Metabolic disorders (acidosis, alkalosis).
· Endocrine disorders (hyperthyroidism, hypothyroidism).
· Disturbance of heart rhythm caused by heart failure.
· Heart rhythm disorders since karmiopati or cardiac tumors.
· Disturbance of heart rhythm due to degeneration disease (fibrosis of the cardiac conduction system).
Treatment of Arrhythmias:
In principle purpose of arrhythmia therapy are (1) to restore normal heart rhythm (rhythm control), (2) lower heart rate (rate control), and (3) to prevent blood clots.
Drugs that can be used are classified by the Vaughan Williams:
• Class 1: Class Insulation Na
- He: Quinidin, Procainamid, Disopyramid
- Ib: lidocain, Mexiletin, Phenitoin
- Ic: Propafenon, Flecainamid.
• Class II: Beta blockers Gol à Propranolol, Bisoprolol
• Class III: Gol. Pot prolonging drugs. Action and repolarization (Most Secure) àAmiodaron, Sotalol, Bretilium
• Class IV: Gol.Ca - àVerapamil Antagonist, Diltiazem
B. Congestive Heart Failure
Clinical symptoms are caused by a weak pump "can not meet the needs of the body continuously for oxygen and nutrients. Inability of the heart to pump blood in sufficient quantities for the body's metabolic needs. As a result of:
· Cardiac wall stretching to hold more blood
· Walls of the heart muscle to thicken to pump more strongly
· The kidneys causes the body to retain fluid and sodium. This adds to the amount of blood circulating through the heart and blood vessels.
· Your body tries to compensate by releasing hormones that make the heart work harder. With time, this replacement mechanism fails and the symptoms of heart failure began to emerge. Like an overstretched rubber band, then the heart's ability to stretch and shrink back will be reduced. The heart muscle becomes excessively stretched and can not pump blood efficiently.
Symptoms:
The main symptoms that occur vary among some people. A recurring symptoms are shortness of breath (especially when on the move) and the fatigue that causes interference with physical activity being undertaken.
Treatment of Congestive Heart Failure:
* Diuretic
* Angiotensin Receptor Blocker
* Digoxin
* Beta blockers à Propranolol, Bisoprolol
C. Angina
Angina is chest pain or discomfort that occurs when not enough oxygen-rich blood flow to the heart muscle. The pain may also occur in the shoulder, arm, neck, jaw, or back. Condition originated from the condition in which there is a plaque (plaque) that forms in the coronary arteries. While functioning heart blood vessels supplying blood to the heart muscle with blood rich in oxygen. In the presence of plaque, the narrowing of coronary arteries so that blood flow to the heart muscle is reduced. As a result, the oxygen supply is reduced. If blood flow to the heart is completely blocked. This condition is called angina or heart attack. Without rapid treatment, heart attack can lead to serious problems and even death.
Three types of angina:
· Stable angina: angina type caused by an imbalance between the need for the blood of the heart and the amount of available oxygen. "Stable", means the same activity that caused him; taste the same every time, and subsides with rest and / or oral medications. Stable angina is a warning sign of heart disease, and should be evaluated by a doctor. If the pattern of angina changes, it can increase to non-stable angina.
· Unstable Angina: The type of angina is considered an acute coronary syndrome. May be a new symptom or a change from stable angina. Angina may occur more frequently, more easily appear at rest, feel more severe, or lasts more lama.Meskipun angina can often be relieved with oral medication, but is not stable and may be aiming to increase the heart. Usually it takes a more in-depth medical treatment, or a procedure needs to be done. Of unstable angina is an acute coronary syndrome, and should be treated as an emergency.
· Variant angina (coronary spasm): Coronary artery spasm can be, which interferes with blood flow to the heart muscle (ischemia). It occurs in people without significant coronary artery disease, however, two thirds of people with variant angina have severe disease in at least one vessel, and spasm occurs at the site of blockage. Type of angina is not common and almost always occurs when a rest - during sleep. You have increased risk for coronary spasm if you have: underlying coronary artery disease, smoking, or using stimulants or drugs (like cocaine). If the artery spasm is severe and occurs for a long time, a heart attack can occur.
Symptoms: - Chest pain
Treatment of angina:
- Non-pharmacological therapies : Set the pattern of life by reducing smoking,
- Pharmacological therapy :
1. Beta blockers à Propranolol, Bisoprolol
2. ISDN à nitrate, nitroglycerin (NTG),
3. Calcium Channel Antagonist à verapamil, diltiazem
4. À antiplatelet aspirin, ticlopidine, clopidogrel, warfarinjantung
- Pharmacological therapy :
1. Beta blockers à Propranolol, Bisoprolol
2. ISDN à nitrate, nitroglycerin (NTG),
3. Calcium Channel Antagonist à verapamil, diltiazem
4. À antiplatelet aspirin, ticlopidine, clopidogrel, warfarinjantung








0 comments: